Archives
Population Health Research Design
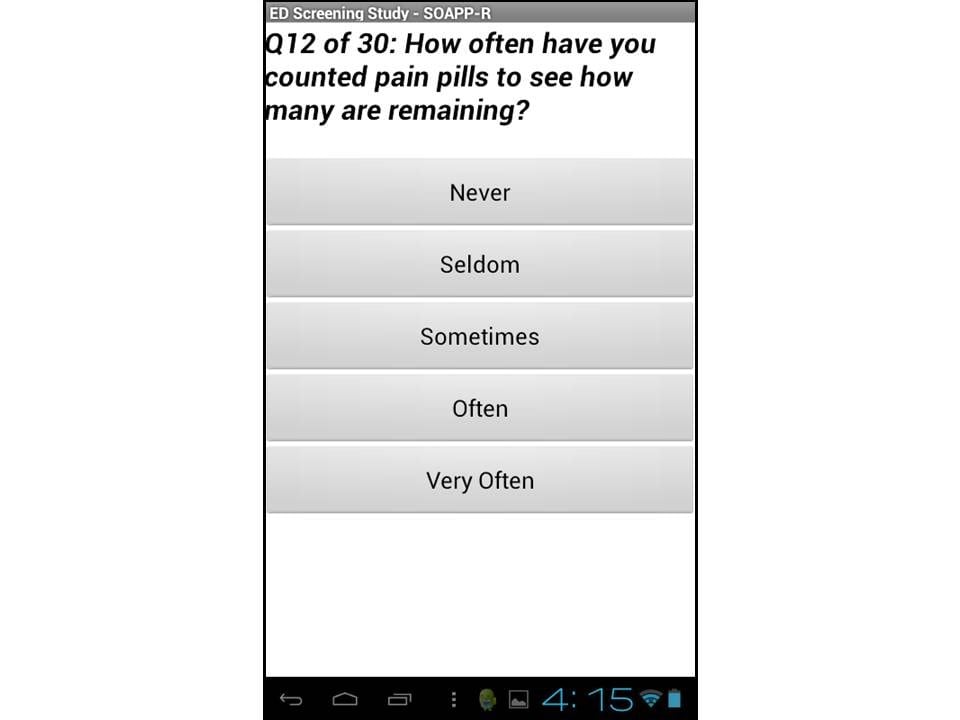
Feasibility of Tablet Computer Screening for Opioid Abuse in the Emergency Department
Westjem Read More
Emergency Department Operations
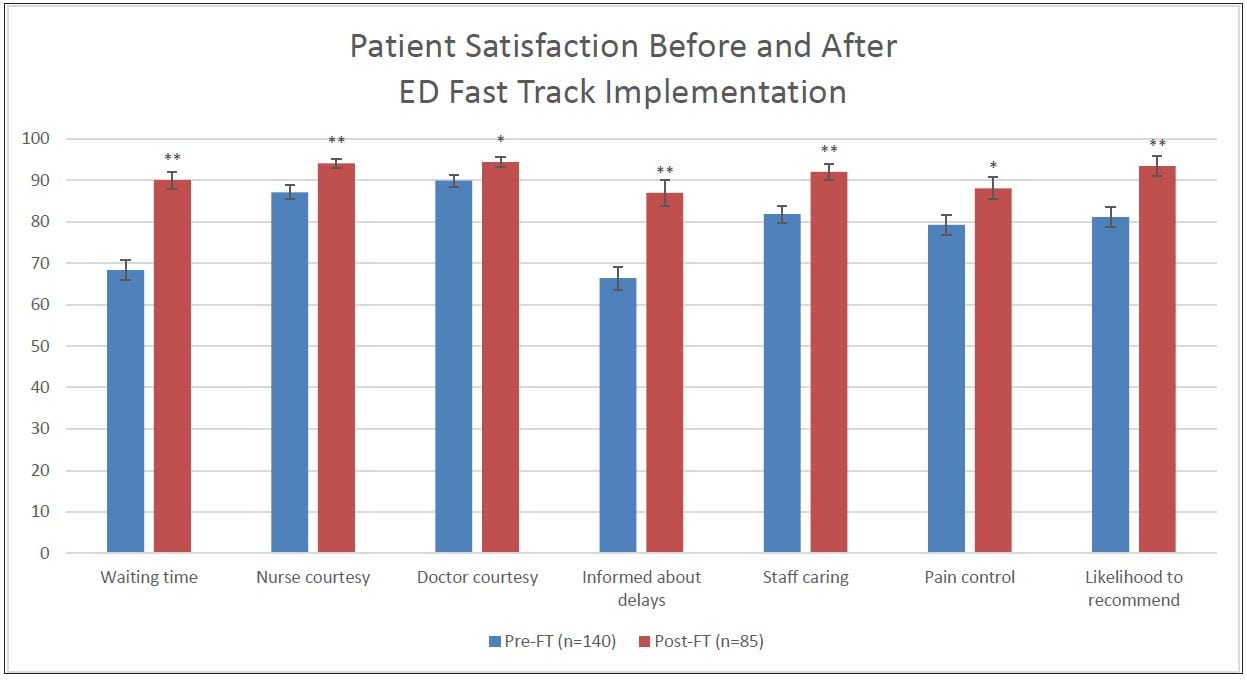
Effect of an Emergency Department Fast Track on Press-Ganey Patient Satisfaction Scores
Westjem Read More
Emergency Department Operations
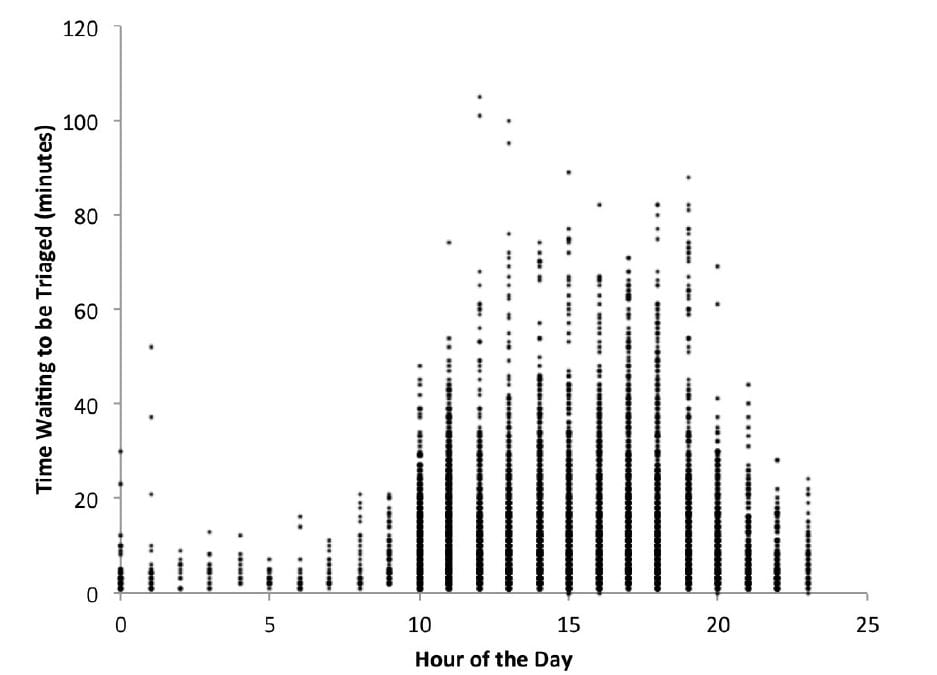
Waiting for Triage: Unmeasured Time in Patient Flow
Westjem Read More
Emergency Department Operations