Volume 14 Issue 5
Discourse in Emergency Medicine and Population Health
In Response to “Temperature and Violent Crime in Dallas, Texas: Relationships and Implications of Climate Change”
WestJEM Read More
Ethical and Legal Issues
Medical-legal Issues in the Agitated Patient: Cases and Caveats
WestJEM Read More
Ethical and Legal Issues
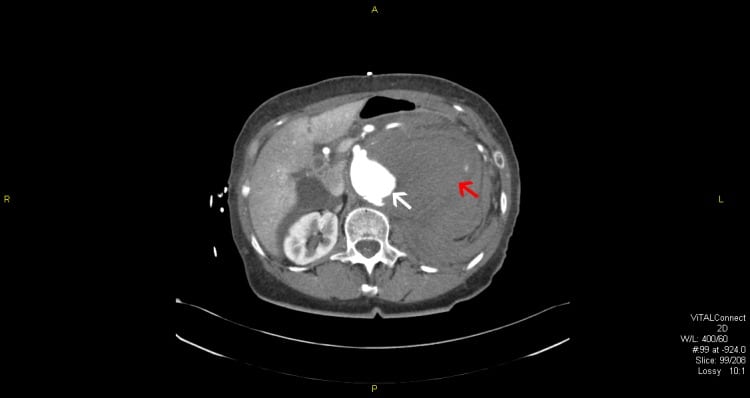
When a Patient Declines Curative Care: Management of a Ruptured Aortic Aneurysm
WestJEM Read More
Emergency Department Operations
Measuring Power in an Emergency Department to Improve Processes and Decrease the Length of Stay to their Optimum Value
WestJEM Read More
Emergency Department Operations