| Author | Affiliation |
|---|---|
| Tommy Y. Kim, MD | Children’s Hospital of Orange County, Department of Pediatric Emergency Medicine Loma Linda University Medical Center and Children’s Hospital, Department of Emergency Medicine, Division of Pediatric Emergency Medicine |
| Maria H. Lin, MD | Children’s Hospital of Orange County, Department of Pediatrics |
| Lilit Minasyan, MD | Children’s Hospital of Orange County, Department of Pediatric Emergency Medicine |
| William N. Holmes, MD | Children’s Hospital of Orange County and MRD Diagnostic Medical Imaging, Department of Radiology |
| Ameer P. Mody, MD | Children’s Hospital of Orange County, Department of Pediatric Emergency Medicine |
A 21-month-old male presented with a low impact fall striking his left eye against a metal stand at the market. On examination he was in no distress, had significant periorbital swelling, a dilated pupil with a sluggish pupillary response, and grossly normal extraocular movements. The initial orbital computed tomography (CT) showed a small nondisplaced fracture of the orbital roof with a fracture around the orbital apex. There was loculated air and hemorrhage within the left orbit, but the globe was intact. There was also an abnormal dense intracranial calcification along the lateral margin of the suprasellar region near the cavernous sinus which was suspicious for a small fracture fragment (Figure 1). A head CT confirmed the finding of a 4–5mm bone intracranial fragment posterior to the left orbital apex (Figure 2).
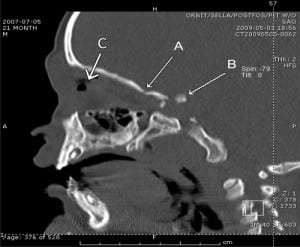
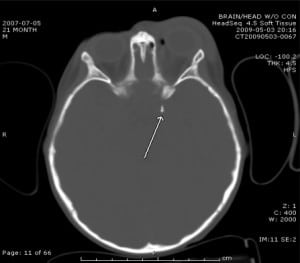
The orbital apex is the most posterior third of the conical orbit and contains the optic canal, superior orbital fissure, and neurovascular structures.1 Fracture of the orbital apex has been shown to result from high-energy trauma.2 They seldom occur as isolated, low impact events, such as in our patient’s case. There are many potential complications involved with orbital apex fractures, including injury to the optic nerve, superior orbital fissure syndrome, and orbital apex syndrome.1The orbital apex involves complex osseous anatomic structures and intimately encloses neurovascular organs that are at risk for permanent damage in an orbital apex fracture. Optic nerve injury may result in loss of visual acuity or immediate blindness. In pediatric patients with head trauma involving the eye, it is imperative to keep in mind the possibility of orbital apex fractures as a potential source of optic nerve damage even in the presence of a low impact injury.
Footnotes
Supervising Section Editor: Sean Henderson, MD
Submission history: Submitted January 12, 2010; Revision Received January 12, 2010; Accepted January 19, 2010
Full text available through open access at http://escholarship.org/uc/uciem_westjem
Address for Correspondence: Tommy Y. Kim, MD, Department of Pediatric Emergency Medicine, Loma Linda University Medical Center and Children’s Hospital, 11234 Anderson St, Loma Linda, CA 92354
Email: tommyyhokim@yahoo.com
Conflicts of Interest: By the WestJEM article submission agreement, all authors are required to disclose all affiliations, funding sources, and financial or management relationships that could be perceived as potential sources of bias. The authors disclosed none.
REFERENCES
1. Linnau KF, Hallam DK, Lomoschitz FM, et al. Orbital apex injury: trauma at the junction between the face and the cranium. Eur J Radiol. 2003;48:5–16. [PubMed]
2. Unger JM. Orbital apex fractures: the contribution of computed tomography. Radiology.1984;150:713–17. [PubMed]